Continuous Cybersecurity Compliance as a Service
Continuous Cybersecurity Compliance as a Service is an approach designed to maintain adherence to regulatory requirements, industry standards, best practices, and internal policies on an ongoing basis.
It involves continuous monitoring, assessment, and remediation of potential issues. The goal is to ensure that an organization's operations and activities remain compliant with applicable rules and regulations at all times.
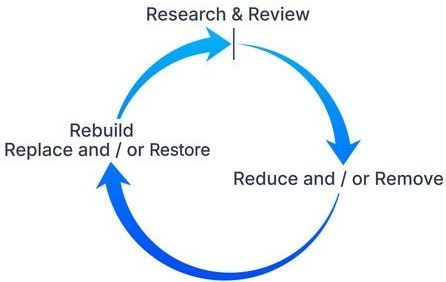
The lifecycle of Continuous Cybersecurity Compliance as a Service includes three main steps:
Review and Research
Reduce and/or Remove
Rebuild, Replace and/or Restore
Key aspects of this approach include:
Automation
Automated processes and tools monitor and assess compliance data, reducing manual workload and allowing teams to focus on addressing and preventing issues.
Real-time monitoring
Systems and processes are continuously monitored to quickly detect compliance issues or vulnerabilities, enabling timely remediation. This proactive approach helps minimize risks.
Risk-based prioritization
Remediation efforts are prioritized based on the risk level of identified issues, ensuring critical problems are addressed promptly.
Integration with existing systems
Solutions integrate with existing IT infrastructure, applications, and security tools for seamless data collection and analysis.
Adaptability
The approach allows organizations to quickly adapt as regulatory requirements and industry standards evolve by continuously monitoring and updating compliance information.
Minimize risks and foster a culture of compliance
In essence, Continuous Cybersecurity Compliance as a Service utilizes automation, real-time monitoring, risk prioritization, integration, and adaptability to help organizations maintain ongoing adherence, minimize risks, avoid penalties, and foster a culture of compliance. The term "Continuous" describes something that happens or exists without interruption or a break, which aligns with this approach.
Continuous Cybersecurity Compliance Auditing
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape with increasingly sophisticated cyber threats, periodic audits are often insufficient.
A continuous audit approach to Cybersecurity Compliance is considered essential for ensuring ongoing compliance and security. Traditional point-in-time audits are no longer enough because cyber threats constantly evolve and compliance requirements are frequently updated. Continuous auditing provides an up-to-date understanding of an organization's cybersecurity posture and ensures ongoing compliance with the latest regulations. By continuously monitoring and assessing cybersecurity controls, organizations can quickly identify and address vulnerabilities before exploitation.
Key features
A Continuous Cybersecurity Compliance Audit Program transforms compliance from a point-in-time exercise into an ongoing, automated, and actionable process. Key features often include:
Real-Time Monitoring & Assessment
This involves automated scanning of IT environments, cloud infrastructure, and endpoints to identify vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and compliance gaps. It also includes real-time mapping to frameworks like NIST 800-53, GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001, PCI-DSS, CMMC, etc. Dynamic reporting, instant dashboards, and alerts track compliance status.
Advanced Analytics and AI
Machine learning can identify potential compliance risks predictively. AI-driven monitoring detects unusual activity indicating violations or breaches. Automated evidence collection streamlines documentation for audits.
Expert Oversight and Support
This includes dedicated compliance advisors who provide guidance on remediation and regulatory updates. Tailored audit plans based on organizational needs are developed. Ongoing employee training helps embed compliance into the culture.
Cost and Time Efficiency
Automation minimizes disruption and reduces audit preparation time. This approach can be scalable. Proactive remediation helps avoid costly penalties and breaches.
The benefits
The benefits of adopting a continuous audit approach to Cybersecurity Compliance include:
Enhanced Security Posture
Provides continuous visibility to stay ahead of threats.
Regulatory Confidence
Demonstrates compliance to regulators, customers, and stakeholders with real-time evidence. It helps organizations stay audit-ready for various frameworks.
Cost Savings
Helps avoid fines, reduces audit costs, and minimizes breach-related expenses. It saves time and resources with automation.
Reputation Protection
Maintaining a strong, compliant security framework builds trust.
Reduced CyberSecurity Insurance
Continuous Compliance can lead to lesser costs
Why Choose Continuous Cybersecurity Compliance
Challenges that necessitate this approach include evolving threats (e.g., 60% of organizations experiencing a breach due to unpatched vulnerabilities/misconfigurations), regulatory complexity with frequent updates, resource constraints making manual audits time-consuming and costly, and reactive approaches from periodic audits that leave gaps in visibility.
A continuous audit framework is not just an enhancement but a strategic necessity to proactively manage risk, maintain trust, and demonstrate ongoing compliance. It allows organizations to move from reactive to proactive compliance.
Financial Costs of Ransomware on US Local Governments
Ransomware attacks on local governments in the USA can result in significant costs, including both ransom payments and recovery expenses.
Beyond direct costs, there are indirect costs such as downtime, lost productivity, and reputational damage. The total cost can be devastating, especially for governments with limited budgets.
Direct Costs
Ransom Payments
These vary widely. Examples include Riviera Beach, FL ($600,000 paid in 2019) and Montclair, NJ ($450,000 settled in 2023). While the average ransom across sectors was $2 million in 2024, local governments often pay less. The trend is shifting away from paying ransoms; only one government entity was reported to have paid in 2022, compared to 43% in 2021.
Recovery Costs
These can range from hundreds of thousands to tens of millions. Baltimore, MD, incurred $18.2 million in recovery costs in 2019 after refusing a $76,000 ransom demand. New Orleans, LA, also faced millions in recovery efforts in 2019. Recovery costs for government entities were estimated at 2–3 times the ransom amount in 2023.
Indirect Costs
Downtime and Productivity Losses
Ransomware attacks on US government organizations caused an estimated $70 billion in downtime costs from 2018–2022. This includes lost productivity, delayed services, and manual workarounds. In 2023, 98% of ransomware attacks on state and local governments resulted in data encryption, leading to an average downtime of 1–4 weeks, costing millions in lost productivity.
Data Breach Costs
Attacks involving data leaks trigger additional costs like identity protection services, legal fees, and public relations efforts. The average cost of a data breach in the public sector was $2.6 million in 2023.
Service Disruptions
Attacks can disrupt essential services like accessing documents, police operations, permitting, tax services, and water billing, increasing operational costs for manual processes and causing economic losses for residents and businesses.
Broader Trends and Estimates:
Frequency
95 government entities were hit by ransomware in 2023, down slightly from 106 in 2022, but 98% of these involved encryptions.
Attack Vectors
Phishing (49% of 2023 attacks), unpatched vulnerabilities, and compromised credentials are common entry points driving costs.
Underreporting
Many incidents are likely underreported, meaning total costs are higher than recorded figures.
Cost Mitigation
Using backups helped governments avoid ransom payments in 70% of 2023 cases, though recovery costs remained significant.
Total Cost Estimates
Per incident costs range from $500,000 to $20 million+. Nationwide, downtime alone was estimated at $70 billion from 2018–2022. An estimate for 2023 suggests total costs for local governments ranged from $190 million to $475 million. Another report estimated US governments paid over $18 billion in costs (downtime and recovery) in 2020 alone.
The financial toll goes far beyond ransom payments; recovery, reputation damage, and operational disruption often cost significantly more, particularly for underfunded municipal IT departments.
Recommendations to Reduce Costs
Regular, offline backups.
Cybersecurity training to address phishing.
Leveraging federal support like CISA's free vulnerability scanning and MS-ISAC resources.
Having predefined incident response plans, which can cut downtime by 30–50%.
Maryland Government Ransomware Costs and Incidents
Ransomware attacks have also led to significant financial losses and operational disruptions for local governments in Maryland.
Specific Maryland Incidents
Baltimore City
May 2019
Targeted by Robbinhood ransomware. Refused the $76,000 ransom demand. Total estimated cost was $18.2 million, including approximately $10 million in recovery expenses and $8.2 million in lost/delayed revenue from disrupted services like property taxes and water billing. The attack severely disrupted city services, and full recovery took months due to outdated backups and lack of a disaster recovery plan. Baltimore purchased $20 million in cyber liability coverage post-attack.
Baltimore County Public Schools
November 2020
Experienced an attack that disrupted online classes and administrative systems. Estimated recovery cost was $7.7 million, potentially exceeding $8 million total. This included over $2 million for cloud migration and over $1.4 million for security software. Cyber insurance covered up to $2 million in direct costs and $3 million for liability.
University of Maryland
2020
Hit by an attack costing over $2 million in recovery.
City of Salisbury
January 2019
Locked the police department network, disrupting operations. Costs were not publicly reported but estimated from hundreds of thousands to low millions. No ransom payment was reported. This attack spurred Maryland's proposed legislation to criminalize ransomware possession.
Leonardtown and North Beach
2021
Small municipalities affected, disrupting essential services like water billing. Specific financial figures are not disclosed, but highlight the vulnerability of smaller governments.
Broader Context in Maryland
Total Known Costs
Known incidents cost Maryland local governments are an estimated ~$18.7–$20.2 million from 2019 alone, primarily due to the Baltimore attack. No major local government attacks were widely reported in Maryland from 2020–2025, though smaller or unreported incidents may exist.
Indirect Costs
Downtime and lost productivity significantly impacted Baltimore's recovery. Baltimore also faced public criticism for poor cybersecurity practices, revealing reputational damage.
Trends
Maryland has seen at least two notable local government attacks. Nationally, attack frequency may be declining slightly. Maryland's 2019 costs were higher than national averages due to Baltimore's scale and lack of preparedness. Attack vectors like phishing were likely involved.
Factors Driving Costs in Maryland
Outdated infrastructure, including lack of modern backups and disaster recovery plans.
Service disruptions impacting critical municipal functions.
Refusing to pay ransoms (as in Baltimore) can increase recovery costs.
Phishing remains a key entry point that lead to compromised credentials.
Recommendations to Reduce Costs
Implementing offline backups, potentially cutting recovery time and costs significantly.
Providing cybersecurity training to address phishing risks.
Considering cyber insurance coverage as Baltimore did post-2019.
Supporting state legislation aimed at deterring attacks.
Utilizing federal support and tools like CISA's resources.
*Data limitations exist, as costs for some incidents (like Salisbury) are not publicly detailed, and smaller or unreported incidents may have occurred after 2019.
These incidents emphasize the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures and preparedness for Maryland local governments.
Cyber Compliance that keeps your business running.
Useful Links
Contact Us
2408867687
Hello@c3aaS.com
All Rights Reserved | Continuous Compliance